

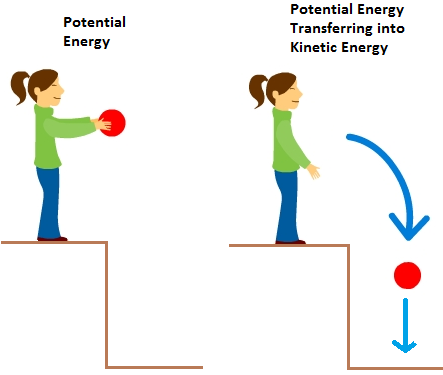
So, in theory, your iPhone actually would look. Potential Energy to Kinetic Energy Particles also have potential energy. Just like your favourite iPhone is made up of many components, all matter is made up of extremely small components called particles. Answer: The total amount of kinetic energy of the moving particles inside the substance is the summation of kinetic energies of all the particles calculated individually keeping in mind every particle may be of different mass and moving at a different velocity. The butter particles begin moving faster and the temperature of the butter increases. They are arranged differently and move in different ways. All matter is made up of many small particles that are constantly in a state of random motion. Gizmos student exploration cell types answer key pdf. The particles in solids, liquids and gases have different amounts of energy. The kinetic energy of a gas particle depends on its molar mass. (a) What is the kinetic energy of an 80-kg athlete, running at 10 m/s? (b) The Chicxulub crater in Yucatan, one of the largest existing impact craters on Earth, is thought to have been created by an asteroid, traveling atĢ2 km/s and releasing 4.2\times, and solve for v.The kinetic particle theory explains the properties of the different states of matter. Since objects (or systems) of interest vary in complexity, we first define the kinetic energy of a particle with mass m. At speeds comparable to the speed of light, the special theory of relativity requires a different expression for the kinetic energy of a particle, as discussed in Relativity in the third volume of this text. Note that when we say “classical,” we mean non-relativistic, that is, at speeds much less that the speed of light. (7) Kinetic energy of the system of particles Let there are n number of particles in a n particle system and these particles possess some motion. As shown in 1, the kinetic energy of a system of particles has two terms: the kinetic energy of the CM (T shown in 1) and the sum of the relative. With this history in mind, we can now state the classical definition of kinetic energy. 5.A student wants to collect data during an experiment about the transfer of kinetic energy in a sample of water and ice. 4.An increase in thermal energy leads to ANSWERan increase in heat and an increase in kinetic energy until a phase change occurs.
(If you have ever played billiards or croquet, or seen a model of Newton’s Cradle, you have observed this type of collision.) The idea behind this quantity was related to the forces acting on a body and was referred to as “the energy of motion.” Later on, during the eighteenth century, the name kinetic energy was given to energy of motion. ANSWERThe potential energy decreases due to the tighter arrangement of the particles. The first body stops, and the second body moves off with the initial velocity of the first body. At the end of the seventeenth century, a quantity was introduced into mechanics to explain collisions between two perfectly elastic bodies, in which one body makes a head-on collision with an identical body at rest. The kinetic energy of a particle and the momentum of each particle in the coating formation must be converted into other forms of energy via mechanisms such as plastic deformation, void consolidation, particleparticle rotation, and strain, and ultimately, heat. This does not depend on the direction of the velocity, only its magnitude. It’s plausible to suppose that the greater the velocity of a body, the greater effect it could have on other bodies.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
